Maxdop
Maxdop stands for max degree for parallelism.
Let's say, the maxdop is set to 4, it means during parallel plan execution, SQL server is going to use 4 processors. If you set your Maxdop settings to 0, it means SQL server is going to use as many processors it needs to complete your request.
So it sounds like keeping maxdop to 0 is good, since more processors mean less processing time, right? It's not true all the time. SO, Let's dig in.
I will be using AdventureWorks2019 Database for the following.
First, I use the following query to find out the size of each of the tables of the database.
SELECT t.NAME AS TableName, s.Name AS SchemaName, p.rows, SUM(a.total_pages) * 8 AS TotalSpaceKB, CAST(ROUND(((SUM(a.total_pages) * 8) / 1024.00), 2) AS NUMERIC(36, 2)) AS TotalSpaceMB, SUM(a.used_pages) * 8 AS UsedSpaceKB, CAST(ROUND(((SUM(a.used_pages) * 8) / 1024.00), 2) AS NUMERIC(36, 2)) AS UsedSpaceMB, (SUM(a.total_pages) - SUM(a.used_pages)) * 8 AS UnusedSpaceKB, CAST(ROUND(((SUM(a.total_pages) - SUM(a.used_pages)) * 8) / 1024.00, 2) AS NUMERIC(36, 2)) AS UnusedSpaceMB FROM sys.tables t INNER JOIN sys.indexes i ON t.OBJECT_ID = i.object_id INNER JOIN sys.partitions p ON i.object_id = p.OBJECT_ID AND i.index_id = p.index_id INNER JOIN sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_id LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.schemas s ON t.schema_id = s.schema_id WHERE t.NAME NOT LIKE 'dt%' AND t.is_ms_shipped = 0 AND i.OBJECT_ID > 255 GROUP BY t.Name, s.Name, p.Rows ORDER BY TotalSpaceMB DESC, t.Name
This outputs something like this -

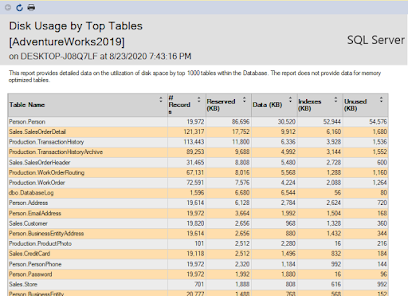
Alternatively, we can use the built reports of SQL Server to find out the size of the tables. For this you need to go to DatabaseName-> Right Click -> Select Report -> Disk Usage By Top Tables
This will output something like this
What is the recommended settings for Maxdop?
- 8 or less processors ===> 0 to N (where N= no. of processors)
8More than 8 processors ===> 8- NUMA configured ===> MAXDOP should not exceed no of CPU’s assigned to each NUMA node with max value capped to 8
- Hyper threading Enabled ===> Should not exceed the number of physical processors.
declare @hyperthreadingRatio bit declare @logicalCPUs int declare @HTEnabled int declare @physicalCPU int declare @SOCKET int declare @logicalCPUPerNuma int declare @NoOfNUMA int select @logicalCPUs = cpu_count -- [Logical CPU Count] ,@hyperthreadingRatio = hyperthread_ratio -- [Hyperthread Ratio] ,@physicalCPU = cpu_count / hyperthread_ratio -- [Physical CPU Count] ,@HTEnabled = case when cpu_count > hyperthread_ratio then 1 else 0 end -- HTEnabled from sys.dm_os_sys_info option (recompile); select @logicalCPUPerNuma = COUNT(parent_node_id) -- [NumberOfLogicalProcessorsPerNuma] from sys.dm_os_schedulers where [status] = 'VISIBLE ONLINE' and parent_node_id < 64 group by parent_node_id option (recompile); select @NoOfNUMA = count(distinct parent_node_id) from sys.dm_os_schedulers -- find NO OF NUMA Nodes where [status] = 'VISIBLE ONLINE' and parent_node_id < 64 -- Report the recommendations .... select --- 8 or less processors and NO HT enabled case when @logicalCPUs < 8 and @HTEnabled = 0 then 'MAXDOP setting should be : ' + CAST(@logicalCPUs as varchar(3)) --- 8 or more processors and NO HT enabled when @logicalCPUs >= 8 and @HTEnabled = 0 then 'MAXDOP setting should be : 8' --- 8 or more processors and HT enabled and NO NUMA when @logicalCPUs >= 8 and @HTEnabled = 1 and @NoofNUMA = 1 then 'MaxDop setting should be : ' + CAST(@logicalCPUPerNuma / @physicalCPU as varchar(3)) --- 8 or more processors and HT enabled and NUMA when @logicalCPUs >= 8 and @HTEnabled = 1 and @NoofNUMA > 1 then 'MaxDop setting should be : ' + CAST(@logicalCPUPerNuma / @physicalCPU as varchar(3)) else '' end as Recommendations
What can happen if I set Maxdop to 0 (default) ?
You are going to face Threadpool wait - A deadly poison wait for SQL Server sooner or later.
MAXDOP(1) - What does it imply?
MAXDOP(1) simply allows you to execute SQL requests serially, No parallel processing will be done. These are the following things you can achieve by MAXDOP(1)
- Serial Processing
- Processing requests in a single processor
You have to choose MAXDOP(1) intelligently. Since -
- Less chance of Threadpool Wait.
- MAXDOP(1) is going to use more processing time (coz only one processor is used.)
- As a result, the outputs that were fast before, will be bit slow.
When to set Maxdop(1)
- For queries that gets the filters of your page or report
- For queries that cost less (Query Cost)

Comments
Post a Comment