Select *
Select *We often use the Select * to fetch data from tables of SQL Server.
Today, we will see why we should avoid Select *
I will be using AdventureWorks2019 Database for demonstration.
First, we do the following -
Set Statistics IO ON;This will output us how many 8 KB pages SQL server read for our request.
Let's use Sales.SalesOrderDetail table. We use the following query :
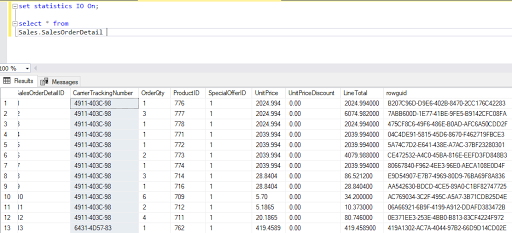
Select *
from Sales.SalesOrderDetail
We get the result tab and Message tab. If we look into the Message tab, we get -
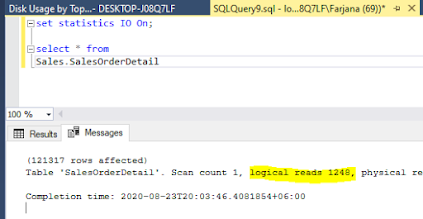
(121317 rows affected)
Table 'SalesOrderDetail'. Scan count 1, logical reads 1248, physical reads 0, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 0, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Ok! SQL Server had to read 1248 - 8 KB pages. you might know, there are 500 pages in a ream of paper. so SQL server had to go through almost 2.5 reams of paper!
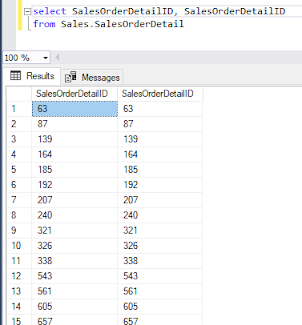
Now, Let's modify our query to select 2 columns
select SalesOrderDetailID, SalesOrderDetailID
from Sales.SalesOrderDetail
Similarly, We get the result tab and Message tab. If we look into the Message tab, we get -
(121317 rows affected)
Table 'SalesOrderDetail'. Scan count 1, logical reads 276, physical reads 1, page server reads 0, read-ahead reads 288, page server read-ahead reads 0, lob logical reads 0, lob physical reads 0, lob page server reads 0, lob read-ahead reads 0, lob page server read-ahead reads 0.
Now, SQL server had to read 276 - 8KB pages, only about half a ream of paper.
Definitely, that's a relief.
Can I use Select * for tables with few columns?
If you need all the columns, select each of the column names instead, Why?
Let's say you have 3 columns on your table, so you decided to Select * instead of writing the names of the column. 2-3 years later, you find out, all other developers have added some columns to the table and the table contains 10/12 columns, and your Select * query that you wrote 3 years ago, is paying off heavily on production server now. So, stay away from the mistake you will probably regret 3 years later.
What can happen if I use Select *
Select * can lead to more processing effort to SQL Server and in case of parallel plan execution enabled, you may face Threadpool - a deadly poison wait for SQL Server.
No worries, to get rid of this deadly wait, all you need is setting your MaxDop and Cost threshhold for parallelism Properly
Remember, the best way to deal with your SQL Server is to think like SQL Server and using the best configuration for your System.


Very informative and easy to CATCH!
ReplyDeleteKeep it up sir :)
Jazakallah :)
I am pleased that you liked it. Stay tuned for more of my SQL Server Pain Reliefs !
Delete